

The Birth of the Federal Reserve
The Hidden Hand of the Rothschild Family
A Brief History of Money
Presently, a lot of dollars are being dumped around the world as new trading routes for ships are commencing to new destinations. The economy has slowed down to a point where volatility is an issue on the markets, and the need for stabilization is at hand. The movement from a World Reserve Currency to an Asset Backed Global Digital Economy is underway. A huge shift has been taking place in the markets since early 2021. Movement into the metal markets has gained traction, and there is a clear path for a conception into the new gold standard economy that will formulate new patterns on the market.
Yes, a reset has been determined and implemented.
This does not mean everything will be fixed in a few days, but a change in our global economic operational system has commenced. Right now, we have a new digital economy in place, and it is in the process of being implemented through e-commerce trade on a Cross Border Trading Computer Platform. It is backed by a Basel 3 gold-backed digital banking system. And, the movement into Basel 4 is at the starting gate whereby revaluations on every sector of the market begins.
Investors Losses: Well, anyone holding US debt would suffer total losses, including central banks, pension funds, governments etc. This would destroy confidence in the financial system… Everyone who has been asking about 401ks or retirement here is your answer.
Economic Crisis: The US government’s ability to fund operations and debt would be crippled, undermining the dollar’s reserve status. This could cause a deep recession or depression. Remember we are going on the Gold Standard. The dollar has to lose value in order for the Iraqi Dinar to become at least 1:1. This is about currency parity. Equal playing field.
Banking collapse: Banks hold huge Treasury reserves – deleting this asset base would trigger bank failures, bail-ins, and potentially wipe out savings. This is why I told you all to put your money in Basel 3 Compliant banks for months. Which is why I said certain banks do not have until 2025 to implement ISO-20022. I stand by that. This is not an olive basket. 2025 is for those banks left over.
Policy Chaos – The Federal Reserve and central banks worldwide would be thrown into chaos as a core pillar of global finance vanished. Emergency measures will not do them any justice in this case. Why do you think I have been constantly telling you all that the US Treasury have been running things? This situation was planned. How? Devolution. Where have you heard over the years that gold will end the Federal Reserve?
Market Instability – Taking the world’s benchmark risk-free asset off the books would of course massively disrupt debt markets and interbank lending, creating extreme volatility. US Treasurys are considered the safest asset out there. They are the foundation that the whole house of cards is built on. If you remove that foundation, the stability of all the markets gonna come crumbling down understand?
-Ariel on X.com
Blockchain refers to an entire network of distributed ledgers, books, or other collections of financial accounts that rely on a particular type of technology. These digital ledgers are incorruptible. They can also be programmed to record and track not only financial transactions but virtually everything of value, creating a shared, distributed, and immutable record of the history of transactions.
The beauty of blockchain is that It is almost impossible to interfere with it. Blockchain is secured through a process known as hashing, which serves as a digital fingerprint for a certain set of data. The same data will always produce the same hashed value. Trying to tamper with a block within a blockchain causes the hash of the block to change. That change makes the following blocks, which are linked to the first block’s hash, invalid.
The second method of securing blockchain is called proof-of-work (PoW), which serves to slow the creation of the blocks. In Bitcoin’s case, for example, it takes about ten minutes to calculate the required PoW and add a new block to the chain. This timeline makes tampering with a block super difficult because if one interferes with one block, they will need to interfere with all the following thousands of blocks, resulting in hundreds of hours of work, just to change one chain.
A third way blockchains secure themselves is by being distributed. Blockchains don’t use a central entity to manage the chain. Instead, they rely on a peer-to-peer (P2P) network. In public blockchains like Bitcoin, there are no barriers to entry, and everyone is allowed to join. Each member of the ever-growing network is called a validator or a node. When someone joins the network, they get a full copy of the blockchain, which is shared and accessible to all within the open network. In this way, the node can verify that everything is still in order, and all transactions remain transparent.
Because cryptocurrencies don’t rely on a central entity to manage the currency network – such as a central bank, central database, or single, central authority – they can be considered to be decentralized.
Rather than management by a central authority, the currency is managed by the cryptocurrency community and, in particular, cryptocurrency miners and network nodes. For this reason, cryptocurrencies are often referred to as “trustless”, which means that no single party or entity controls how a cryptocurrency is issued, spent, or balanced; and so no single authority must be entrusted with that responsibility.
Yet even in the “trustless” cryptocurrency world, users can still trust that the blockchain contains an accurate, immutable, and unchangeable record of cryptocurrency transactions, because of the security safeguards previously discussed.
Cryptocurrencies have no central bank printing new money. Instead, new currency is generated when “miners” “dig up” new currency according to a preset coin-issue schedule, and release it into circulation in a process called mining.
How do you de-throne a World Reserve Currency?
Fiat Money vs the Gold Standard
A Brief History of Money
What is Quantum Financial System?
The Quantum Financial System (QFS) is a new financial technology that uses quantum computing, quantum cryptography, and blockchain to enable faster, safer, and more democratic money transactions, it’s also cheaper, because there are no middlemen or transaction fees.
The QFS changes the way market systems work together collectively and individually, and why, we are currently going through a Global Currency Reset.
The gold standard is a monetary system where a country’s currency or paper money has a value directly linked to gold.
The appeal of a gold standard is that it arrests control of the issuance of money out of the hands of imperfect human beings.



Cryptocurrency is a virtual currency based on a distributed ledger and enforced by a network of computers. It operates on a decentralized network based on blockchain technology.
Ever wonder why it seems that we work & save yet it seems that we are always having to make choices on what
The Quantum Financial System represents a fusion of advanced technologies, combining quantum computing and blockchain to create a financial ecosystem that promises to redefine how we perceive and interact with money.
It’s not just about adopting new, cutting-edge technology — it’s about reshaping the very foundation of modern finance.
If you are wondering whether the quantum financial system could be a real thing, then the answer is yes. It may sound like science fiction to some people, but this is a very genuine technology.
Today, the primary objective of the Financial Quantum System is to facilitate consistent integrity of the funds’ movement, precisely estimate uncertainty in financial models, and eliminate the shortcomings of the central banking system.
The financial world has evolved a lot in the past 50 years. Not so long ago, the most common way to pay while buying something was to use cash. Now we have plenty of options. Use a debit/credit card or pay with an app or cryptocurrency wallet on your smartphone. The choice is yours.
Today, the 30 largest banks in the world manage more than $65 trillion combined. According to the Bank for International Settlements, the size of the bond market is over $130 trillion worldwide and $51 trillion for the US market.
In this complex market, a vast number of financial services activities (ranging from securities pricing to risk analysis) are performed every second. Each activity requires the ability to assess short-term and long-term outcomes.
To do this, financial institutions utilize advanced algorithms and machine learning models that measure statistical probabilities. However, these models are not completely accurate — we all saw what happened during the 2008 financial crisis.
The current technology still needs to mature in many ways to fulfill promises. Thus, several financial companies are testing new processors that leverage the laws of quantum physics to process massive volumes of data at unprecedented speed. The possibilities are endless.
Quantum machines can revolutionize industries that require enormous computing power, including discovering new medicines, empowering deep neural networks, modeling financial markets, and developing a secure way of communication (quantum internet).
In this article, we have focused on how quantum computers can improve current financial systems.
Banking sectors, non-banking financial companies, hedge funds, and other financial institutions deal with very sensitive data like customer transactions and contracts. This data needs to be kept private and secure for a longer period of time.
Many banking activities, such as security pricing, involve a high degree of computational complexity. This complexity further increases when dealing with pricing options because it requires adapting to rapidly changing market conditions.
Thus, financial institutions are always looking for ways to efficiently determine the price of stock options while keeping the customers’ data secure. The research has shown that quantum computing has great potential to solve such critical financial problems.
When it comes to simulating quantum mechanics and other algorithms, such as Grover’s algorithm for quantum search and Shor’s algorithm for factorization, Quantum computers can easily outperform classical computers.
The working principle of quantum computers is based on quantum physics, which shows that certain properties of particles remain in two different states, or any combination of two states, at any given time. Unlike classical computers that work on dualistic processing systems (0s and 1s), quantum machines can simultaneously be 0 and 1, or a blend of 0 and 1.
Since the quantum system can exist in multiple states at the exact same time (this phenomenon is called superposition), it can perform far more complicated tasks that are beyond the scope of classical supercomputers. This opens the exploration of vast computational possibilities.
The outcomes of quantum computation are also different from their binary counterparts. They are probabilistic (instead of deterministic), which means outputs can differ even if the input remains the same. Thus, the same computation must be done several times to make sure its results converge toward a mean.
While classical computers work with bits, the basic unit of quantum information is called a qubit (or a quantum bit). It can be engineered as photons, electrons, or nuclei.
Examples include the polarization of a photon in which the two states can be the ‘horizontal polarization’ and ‘vertical polarization,’ or the spin of an electron in which two states can be ‘spin up’ and ‘spin down.’
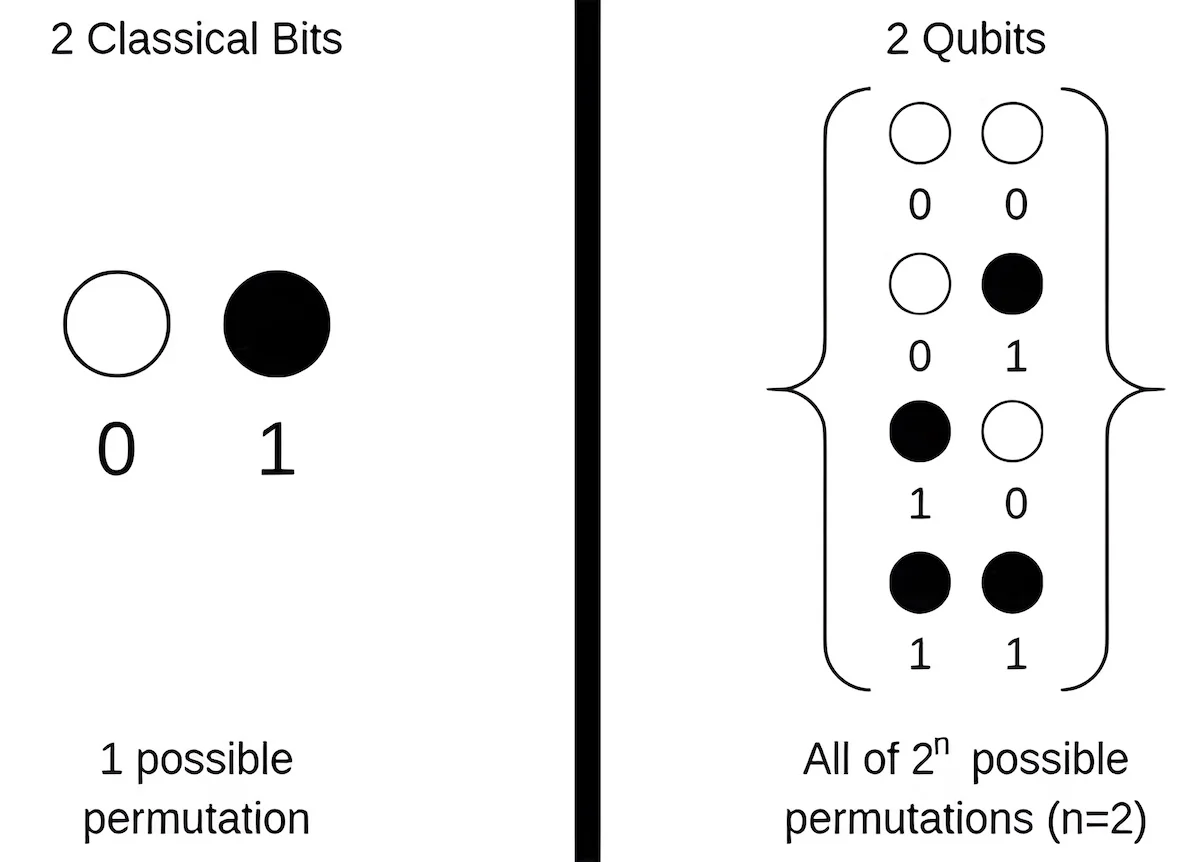
As per the quantum laws, a qubit can be in a coherent superposition of both states at the same time. For example, a two-qubit quantum computer could have ’00’ ’01’ ’10’ ’11’ states. A classical computer would require 4 bits to achieve this.
Similarly, 3 qubits can be the same amount as 8 binary bits, 4 qubits the same as 16 bits, 5 qubits the same as 32, 6 qubits the same as 64, and so on.
To put this into perspective, a 300-qubit system can have more states than the total number of atoms in the universe. Even the most powerful classical supercomputer could never process that amount of data.
That is why financial institutions are showing a great interest in quantum computing. While no quantum machine is yet advanced enough to perform tasks that a classical computer can’t, great progress is underway.
In the standard model of banking, money is recognized in three different forms: commodity money, fiat money, and fiduciary money.
We have also seen the rise of cryptocurrencies in the past decade, but it is not yet widely recognizable. It’s a digital payment system that doesn’t have any central issuing or regulating authority. Instead, it is based on a distributed public ledger known as the blockchain, a record of all transactions held by currency holders.
Quantum money takes things to the next level. It applies quantum cryptographic protocol to generate and validate currencies. Since arbitrary quantum states cannot be perfectly copied, it is impossible to forge quantum money.
The idea looks great on paper, but it is not feasible to implement with current technology. This is because quantum money requires us to store the arbitrary quantum states in quantum memory, a quantum-mechanical version of conventional computer memory.
Although years of research and experiments have enabled quantum memory to store qubits, it can do so only for a very short time. Many research institutes across the world are working on new materials to create memories that could hold the quantum information carried by light.

In contrast to traditional computers, where doubling their power demands roughly twice the number of transistors, quantum computers can double their power with just one additional qubit. This makes them especially advantageous for early adopters who can harness this efficiency to their benefit.
Quantum computing has the potential to empower financial institutions to address highly specific business challenges and potentially redesign certain operational processes in the coming decade.
1. Customer targeting and prediction modeling: Quantum computers are exceptionally good at finding hidden patterns in complex data structures, performing classifications, and making accurate predictions.
2. Fraud detection: Each year, financial institutions suffer substantial revenue losses, ranging from $25 billion to $50 billion, due to fraud and poor service management practices. Existing fraud detection systems are not that reliable. They return 80% false positives, causing the banking sector to remain at risk most of the time.
Quantum computing may offer a definitive edge in the battle against payment fraud. Its ability to harness exponential speed through quantum superposition and entanglement offers the potential to reevaluate many potential solutions, ultimately leading to the optimization of fraud detection algorithms.
3. Client management: Quantum computing can transform client management in the financial sector by improving data analysis, security, risk management, operational efficiency, and personalization. This can lead to a seamless and highly satisfying customer experience.
4. Portfolio management: Quantum computing has the potential to speed up asset-pricing models and cultivate performance improvements. It can make a myriad of optimization calculations in a fraction of the time without using approximations.
Its combinatorial optimization capabilities could help investors improve portfolio diversification, rebalance portfolio investments according to the market conditions and end goals, and efficiently streamline trading settlement processes.
5. Enhanced Security: Since QFS employs quantum encryption (an ultra-secure technique that leverages the properties of quantum physics), it can offer unparalleled security, making it extremely resistant to data breaches and financial theft.
6. Decentralization: QFS promotes decentralization, minimizing the reliance on intermediaries and lowering transaction costs. It is also designed to be accessible globally, which means individuals and entities can engage in cross-border transactions more easily.
7. Smart Contracts: QFS supports smart contracts — these are automated agreements (encoded into computer programs) that execute themselves when predefined conditions are met. They eliminate the potential for human error, minimize the risk of disputes, and reduce the need for trust in intermediaries.
8. Reduced Settlement Risk: It is the risk that one party in a financial transaction may not meet its obligations, which may eventually lead to a failure in the settlement process. QFS mitigates this risk through near-instantaneous transactions, smart contracts, and blockchain technology that maintains a transparent and immutable ledger of all transactions.
9. Integration with Artificial Intelligence: QFS can leverage AI algorithms to improve data analytics, risk assessment, and decision-making. It can also interact with IoT devices to provide real-time data on assets, supply chains, and more.
Progress made in the last ten years towards quantum supremacy proves that quantum computers are more capable of solving some specific problems than any conventional computers.
In 2014, for example, a team of researchers from the Netherlands harnessed the capabilities of quantum mechanics to develop a fraud-proof technique for authenticating a credit/debit card that is virtually impossible to thwart.
In 2018, Canadian researchers published a quantum algorithm for the Monte Carlo pricing of financial derivatives, demonstrating a method to create relevant probability distributions in quantum superposition and a technique to extract the price of financial derivatives through quantum measurements.
In 2020, David Orrell proposed a binomial option pricing model based on a quantum walk that can be run directly on a quantum device. In the same year, D-Wave quantum computers were used to solve the Portfolio Optimisation problem. The results were very promising: the performance of the D-Wave hardware (though limited in size) is comparable to superfast classical computers.
In 2021, a group of researchers developed quantum algorithms for high-frequently statistical arbitrage trading by using variable time condition number estimation and quantum linear regression.
In 2023, researchers at IBM Quantum, in collaboration with the University of California, Berkeley, and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, conducted an experiment to test the capabilities of a 127-qubit quantum computer against a state-of-the-art supercomputer. They found that despite the noise issues, quantum computers have the potential to excel in specific computational tasks.
.
Quantum computing technology isn’t fully developed yet. In fact, most of its benefits and applications are still conceptual. Thus, the whole banking sector is left with two choices:
The second option seems better. Many investment banks and financial services holding companies, including JPMorgan Chase, HSBC, and Wells Fargo, have already started pouring millions of dollars into quantum research and innovation programs.
A large body of research and engineering work has been dedicated to the realization of quantum algorithms with substantial polynomial speedups in data-loading and data data-processing subroutines.
So far, no practical application of quantum computing with exponential speedup over its classical counterpart has been invented, but numerous promising models have been proposed.
IBM, for example, has managed to pack 127 qubits in its proprietary quantum-computing chip. The processor uses multiple layers to host signal-carrying wires, which allow precise readouts of the qubits. Although the technique is common in classical chips, it’s a huge achievement in the world of quantum computing.
It is expected that quantum computers will surpass the capabilities of classical computers by the end of 2030. Tech giants, including IBM and Google, are working on quantum machines that can hold hundreds of quantum bits. IBM has made its aspirations more concrete by releasing a blueprint for the development of quantum computers, which includes the aim of developing a 1000-qubit computer.
This will have a disruptive impact on numerous industries, particularly finance. In fact, finance is estimated to be the first sector to benefit from quantum computing in the short and long terms.
Some financial organizations have been actively studying and experimenting with quantum and blockchain technologies. The most popular ones are
JPMorgan Chase, in collaboration with QC Ware, completed a study specifically focusing on the application of quantum techniques to “deep hedging.” Deep hedging is a financial practice used to reduce risk in portfolios by employing data-driven models that take into account market frictions and trading constraints.
HSBC is the first bank to become part of a quantum-secured metro network established by BT and Toshiba. This network employs Quantum Key Distribution, a cryptographic technique that leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to create highly secure encryption keys. The bank is also working with Amazon Web Services to explore quantum-secured communication and data transfer in the context of AWS edge computing.
Wells Fargo‘s developers have published a series of research papers, with more to come, that outline algorithms and software solutions designed for use on quantum computers. These papers are not just theoretical concepts but rather practical applications that have been tested on quantum machines.
They have also partnered with IBM, renowned academic institutions like MIT and Stanford University, and quantum-focused companies like QCWare and Oxford Quantum Circuits to advance quantum coding and testing on real quantum computers.
Goldman Sachs has undertaken well-defined benchmark problems in finance and estimated the performance specifications that a quantum computer would need to surpass in order to provide a real advantage. They have partnered with Quantum Science Laboratory and Amazon Web Services to evaluate various applications of quantum computing to address real-world financial problems.
The future advancements of quantum computing within banking and financial institutions are not without challenges. Following are the major things that have to be dealt with in coming years:
In addition to these challenges, we also need to identify what problems quantum machines can efficiently solve, improve the interface for better accessibility, and extend the interest in quantum computing beyond the elite group of physicians and mathematicians.
Addressing these challenges and adopting quantum-based solutions is not a short-term process. It’s a long-term journey, and it depends on the financial sector’s capability to define problems, adjust the infrastructure, and involve skilled personnel in the process.
A quantum algorithm is a step-by-step instruction, where each step can be performed on a quantum computer. The term ‘quantum’ is used for those algorithms that utilize some basic features of quantum computations, such as quantum entanglement or quantum superposition.
These algorithms can be applied in various fields, including search and optimization, cryptography, solving large systems linear equations, and simulation of quantum systems. The five most popular quantum algorithms are —
The era of the quantum financial system is about to begin. Within the next decade, quantum computing will most probably become one of the mainstream solutions in the finance sector.
According to Spherical Insights, the quantum computing market size will exceed $143 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 26.5%. The early adoption of quantum-based technologies in the finance sector is expected to fuel the market’s growth worldwide.
J.P. Morgan, Goldman Sachs, Citigroup, Mitsubishi Financial Group, Barclays, Wells Fargo, BNP Paribas, HSBC, and Japan Post Bank — they all are pouring millions of dollars into this technology; some have started experimenting with quantum computing applications.
Yes, there are a lot of opportunities available for investors who want to bet on quantum computing technology. A number of companies working in this area are listed on the New York Stock Exchange. A quantum computing ETF (named defiance quantum ETF) is also available to get more general exposure to this industry.

Basel III is an internationally agreed set of measures developed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision in response to the financial crisis of 2007-09. The measures aim to strengthen the regulation, supervision and risk management of banks.
Basel III is an international regulatory accord that introduced a set of reforms designed to mitigate risk within the international banking sector by requiring banks to maintain certain leverage ratios and keep certain levels of reserve capital on hand. Begun in 2009, it is still being implemented as of 2022.
Basel III is an international regulatory accord that introduced a set of reforms designed to improve the regulation, supervision, and risk management of the banking sector.
A consortium of central banks from 28 countries devised Basel III in 2009, largely in response to the financial crisis of 2007–2008 and ensuing economic recession.1 As of 2022, it is still in the process of implementation.
Protocol 20 codes are currently being integrated onto the QFS. These codes deal with currency protocols allowing digital assets to move through the system.
These are necessary, to run the stablecoins which represent a country’s currency. This will increase money velocity and demand. Demand increases value for all the currencies in that country.
Protocol 19
(REGULATION and Transfer Of Wealth)
Protocol 20
(Merging of QFSystems)
These two protocols are happening as we speak. I have been witnessing many changes this week in the crypto space as the digital economies from many platforms all over the world are merging into one single quantum financial system.
As far as the banking system and the markets are concerned, this is the revaluation process taking place at this time through a digital economy allowing cross-border international trade to be possible.
At the conclusion of this new financial setup, you will begin to see the currencies in paper form find their real values due to the increased demand upon each country’s currencies in the digital space.
This new money velocity creates more value over time and real value based upon actual calculated data through artificial intelligence inside a quantum computer regulating and implementing real time values at the point of sale.
* Goldilocks

The Protocol 20 codes integration into the Quantum Financial System (QFS) doesn’t simply echo the march of technology but signals a revolutionary epoch in our financial order. This monumental change is set to recalibrate the very essence of money, shaking the established order to its core, and thrusting us into a new golden age. Strap in, the ride promises to be turbulent, dramatic, and profoundly transformative.
– Protocol 19 is all about the incoming ISO20022 Regulation and those 3 or 4 others below it. It is also about Liquidity.
– Protocol 20 is a complete Transformation to QUANTUM TECHNOLOGIES and it is well under way being installed all around the world and Canada was the most recent this week.
Whiplash347
Blockchain is a type of shared database that differs from a typical database in the way it stores information; blockchains store data in blocks linked together via cryptography.
You might be familiar with spreadsheets or databases. A blockchain is somewhat similar because it is a database where information is entered and stored. But the key difference between a traditional database or spreadsheet and a blockchain is how the data is structured and accessed.
A blockchain is distributed, which means multiple copies are saved on many machines, and they must all match for it to be valid.
The blockchain collects transaction information and enters it into a block, like a cell in a spreadsheet containing information. Once it is full, the information is run through an encryption algorithm, which creates a hexadecimal number called the hash.
The hash is then entered into the following block header and encrypted with the other information in the block. This creates a series of blocks that are chained together.
Blockchain can be used to immutably record any number of data points. This could be in the form of transactions, votes in an election, product inventories, state identifications, deeds to homes, and much more.
The nature of blockchain’s immutability means that fraudulent voting would become far more difficult. For example, a voting system could work such that each country’s citizens would be issued a single cryptocurrency or token.
The new International Payment System ISO20022 is an important and final step in the QFS.
Why?
It is backed by the metal market and brings in the final touches to the digital asset backed Financial System.
ISO20022 is a messaging protocol that defines a standardized way for financial institutions to exchange information about payment transactions. It specifies the format, structure, and content of the messages that are sent between different systems and platforms.
ISO20022 was developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in collaboration with the financial industry. It is designed to be flexible and adaptable, allowing it to be used across a wide range of financial services and transaction types.
The standard includes a variety of message types that cover different types of financial transactions, such as payments, securities, and foreign exchange. Each message type includes specific fields and data elements that must be included in the message, ensuring that the information is consistent and complete.
ISO20022 is also designed to be extensible, meaning that it can be customized to meet the specific needs of different financial institutions and payment systems. This flexibility allows financial institutions to use ISO20022 messaging while still maintaining their own unique systems and processes.
ISO20022 offers a number of benefits for financial institutions and the wider financial industry. Some of the key benefits include:
XRP can be sent directly without needing a central intermediary, making it a convenient instrument in bridging two different currencies quickly and efficiently.
Uphold is the most popular exchange for US customers.
How to move your XRP from Uphold to a Cold Storage Wallet – Ledger
Where to Buy a Cold Storage Wallet
It’s already one of the largest cryptocurrencies, and it could have serious untapped potential.
Ripple could prove to be extremely useful. International money transfers between banks can be slow, expensive, and difficult to even set up. Ripple solves those problems, and it has already secured hundreds of partnerships, including many with major financial institutions. There’s also a large company behind Ripple that’s focused on promoting it and moving it forward.
BRICS is an acronym for Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. The term was initially created as BRIC (without South Africa) by Goldman Sachs economist Jim O’Neill in 2001. He believed that by 2050 the four BRIC economies would come to dominate the global economy. South Africa was added to the list in 2010.
The BRICS countries operate as an organization that seeks to further economic cooperation amongst member nations and increase their economic and political standing in the world.
Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa ranked among the world’s fastest-growing emerging market economies for years. This was thanks to low labor costs, favorable demographics, and abundant natural resources at a time of a global commodities boom.
The group has a set of joint priorities including:
Fast Fact: According to BRICS, the GDP of their nations accounts for 31.5% of global GDP as of 2023, compared to the 30.7% of the G7 nations.4
The overarching goals of BRICS are cooperation, development, and influence in international affairs. Drilling down, BRICS seeks to build economic cooperation, development financing, political coordination, social and cultural exchanges, technology and innovation, sustainable development, and peace and security.
BRICS sees itself as countering the traditional Western-led global order, with some member states viewing the organization as a way to boost their influence around the world.
Still, the nations may disagree on fundamental factors, such as transparency and a balanced approach, which may hinder the growth of the group.
Disclaimer: None of the creator/s have any credentials that warrants them to give any financial advice whatsoever, this is to include the following advice on any investment regarding cryptocurrency, stocks, bonds, or any other form of investments. You hereby understand & agree that any investment advice should be immediately consulted with your OWN personal financial advisor before investing one single dollar. This document is intended for entertainment purposes only and should only be treated as such. We are just documenting our own personal financial journey and sharing our personal experience. You should take nothing you hear or see in these videos or document as financial advice, and understand that if you do, that you take full responsibility for your own actions, as there is a possibility that you can lose all your money. In the event you do invest money that turns out to be at a loss, you agree to hold the creator(s) of this document with zero liability based on your own actions.